29. HOG Classify
HOG Classify
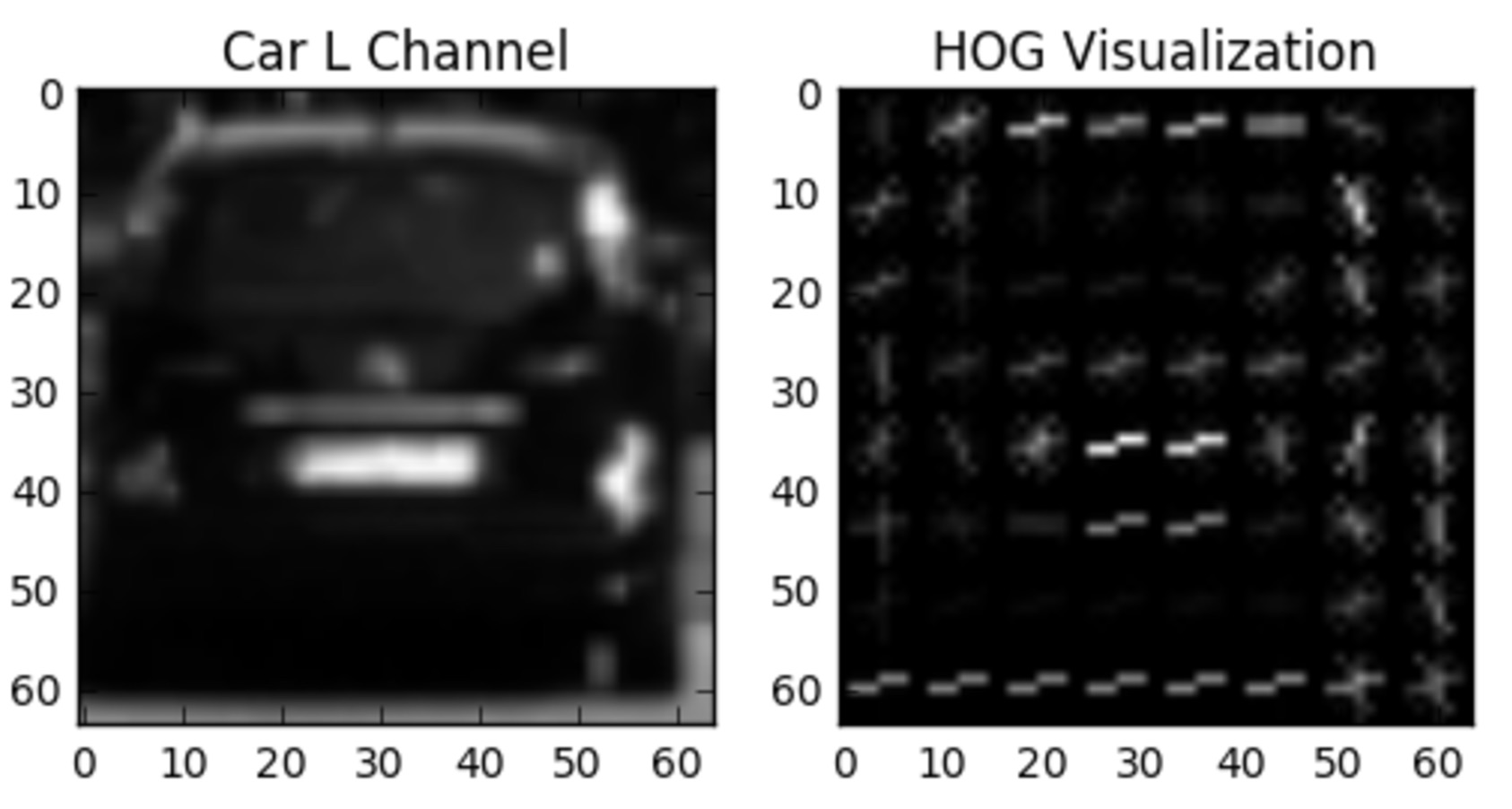
Alright, so classification by color features alone is pretty effective! Now let's try classifying with HOG features and see how well we can do.
NOTE: if you copy the code from the exercise below onto your local machine, but are running
sklearn
version >= 0.18 you will need to change from calling:
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_splitto:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
In the exercise below, you're given all the code to extract HOG features and train a linear SVM. There is no right or wrong answer, but your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to play with the parameters
colorspace
,
orient
,
pix_per_cell
,
cell_per_block
, and
hog_channel
to get a feel for what combination of parameters give the best results.
Note:
hog_channel
can take values of 0, 1, 2, or "ALL", meaning that you extract HOG features from the first, second, third, or all color channels respectively.
Start Quiz: